Cyber threats are rapidly reshaping the digital landscape of healthcare, with attacks ranging from ransomware and phishing to intricate breaches targeting patient records and medical devices. Amid a surge in digitization and remote health technologies, robust cybersecurity is essential to safeguard sensitive health data, secure clinical workflows, and uphold trust in care delivery.
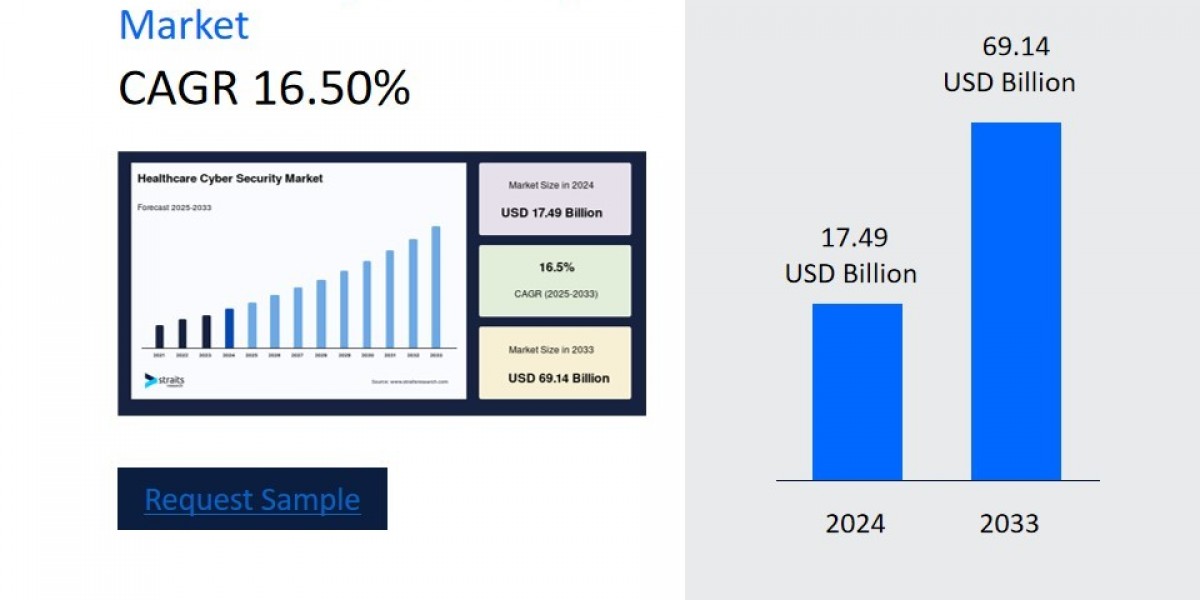
According to Straits Research, the global healthcare cyber security sector was valued at USD 17.49 billion in 2024. It is estimated to reach from USD 20.38 billion in 2025 to USD 69.14 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 16.50% during the forecast period (2025–2033).
Key Trends and Technological Advancements
In 2025, healthcare organizations face a turbulent threat environment powered by sophisticated ransomware, AI-driven phishing, and increased risks from the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Trends shaping the sector include:
Artificial Intelligence: AI-enabled threat detection platforms now monitor vast data streams, instantly recognizing behavioral shifts and unusual access patterns—often uncovering subtle intrusions before humans can react.
Zero Trust Architecture: Rather than assuming anything inside a network is safe, Zero Trust requires continuous authentication, effectively segmenting access to vital systems like health records and devices.
Cloud Security: The migration of sensitive records and administrative tools to cloud environments demands rigorous encryption and compliance with standards such as HIPAA and GDPR. Cloud-native solutions offer scalability but require advanced identity management and constant vigilance against emerging vulnerabilities.
Third-Party Risk Management: Tools like Censinet RiskOps™ and managed security services help organizations monitor vendor security, reflecting a rise in supply chain-related breaches.
Key Players: Regional Insights
Several global technology giants and healthcare specialists have risen to prominence:
IBM (USA): Offers integrated threat intelligence and managed security services to protect healthcare networks, with notable investments in AI-enhanced risk detection.
Cisco Systems (USA): Delivers robust endpoint security and network segmentation solutions, critical for large hospital systems.
Palo Alto Networks (USA): Known for cloud security tools supporting encrypted communications and Zero Trust adoption in hospitals globally.
Zscaler (USA/Global): A cloud-native platform providing healthcare-specific AI threat detection, IoMT device protection, and cost-effective scalability.
CrowdStrike (USA): Renowned for industry-leading endpoint protection and rapid threat mitigation in large health networks.
ManageEngine (India/USA): Focuses on affordable, AI-powered data loss prevention and ePHI detection, supporting both developed and emerging markets.
Censinet (USA): Specializes in third-party risk management tailored for healthcare, now integral to compliance and vendor assessment programs.
Regional and Recent Updates
North America: The United States saw the largest surge in phishing and hacking attacks, with 66 major incidents affecting over 7.1 million people in June 2025 alone. California, Texas, and Florida were hardest hit, while major provider breaches at Episource and McLaren Health Care impacted millions.
Europe: In March 2025, WHO/Europe published a digital health cybersecurity guide, highlighting the need for unified privacy and security standards as the region expands digital health access.
Asia: ManageEngine’s DLP+ tool gained traction in India and Southeast Asia, addressing affordability gaps for mid-sized clinics and hospitals.
Regulation and Compliance
US authorities updated the HIPAA Security Rule in 2025, mandating industry-wide adoption of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and compulsory encryption for all electronic protected health information (ePHI). The new rules eliminate previously optional security controls, pushing for uniform and proactive protection, and harmonize standards with frameworks like NIST and CISA. Healthcare organizations are now expected to:
Employ MFA for access to sensitive systems
Encrypt all ePHI, at rest and in transit
Conduct continuous, organization-wide risk assessments rather than sporadic reviews
News and Industry Developments
June 2025: The largest single breach, at Episource LLC in California, exposed records of over 5.4 million patients. McLaren Health Care (Michigan) and Central Kentucky Radiology faced significant attacks affecting hundreds of thousands of records.
Product Launches: Zscaler introduced new AI-powered modules for IoMT security and compliance, reducing operating costs and improving return on investment for large health networks.
Collaborations: Multiple US and European health systems are increasingly turning to managed security services and cloud infrastructure partnerships to address staff and resource shortages.
Future Outlook
Threats like AI-powered ransomware and IoMT vulnerabilities are expected to intensify, placing a premium on automation, endpoint detection, and real-time monitoring solutions. Managed services will address persistent gaps in internal staffing while regulatory harmonization streamlines cross-border operations. Investment will continue surging as breaches remain frequent and costly—averaging $4.88 million per incident.
Healthcare’s digital transformation thus hinges on blending cutting-edge technology, regulatory compliance, and a culture of continuous vigilance as the foundation for patient safety and trust.